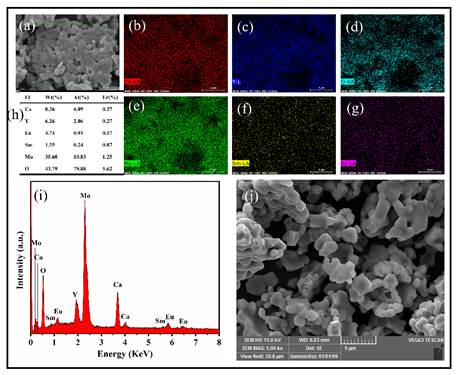
Fluorescent materials play a vital role in modern science and technology, from anti-counterfeiting labels to high-performance coatings and sensors. Among them, rare earth elements such as Europium (Eu³⁺), Samarium (Sm³⁺), and Terbium (Tb³⁺) have gained particular attention because of their sharp emission spectra, long luminescence lifetimes, and excellent stability.
At GESmaterials, we recognize the growing demand for rare-earth-based fluorescent markers in UV-curable coatings and other advanced material systems. Below is an overview of how Eu³⁺, Sm³⁺, and Tb³⁺ are being used in this field.
Why Rare Earth Fluorescent Markers?
- Sharp emission peaks: Unlike organic dyes, rare earth ions provide narrow-band emissions, which make them ideal for precise detection.
- Stability: They exhibit strong resistance to photobleaching and chemical degradation.
- Versatile excitation: Many compounds can be excited with common UV sources, e.g., 355 nm, 385 nm, and 405 nm, which align well with UV curing technologies.
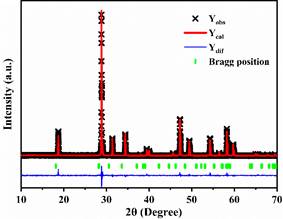
Europium (Eu³⁺): Red Emission Marker
- Emission: Strong red fluorescence (around 612 nm).
- Applications:
- Anti-counterfeiting inks and coatings
- Fluorescent tracers in polymer networks
- Optical sensors and bio-imaging
- Typical compounds: Europium acetylacetonate (Eu(acac)₃), Europium thenoyltrifluoroacetonate (Eu(TTA)₃), and Europium oxide nanoparticles.
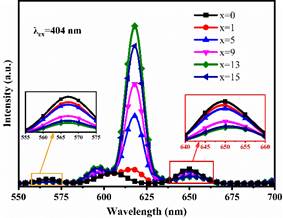
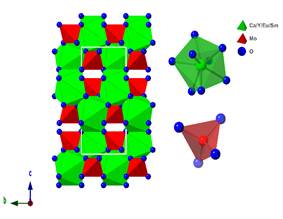
Samarium (Sm³⁺): Orange-Red Luminescence
- Emission: Orange to reddish emission, complementary to Eu³⁺.
- Applications:
- Dual-emission systems when combined with Eu³⁺
- Security coatings requiring subtle fluorescence signatures
- Spectroscopic calibration and reference standards
- Typical compounds: Samarium acetylacetonate (Sm(acac)₃) and other β-diketonates.
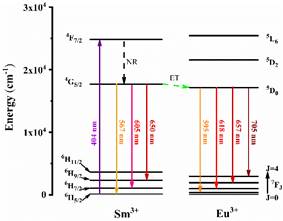
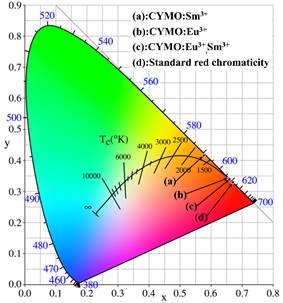
Terbium (Tb³⁺): Green Emission Marker
- Emission: Strong green luminescence (around 545 nm).
- Applications:
- Green security pigments
- Combination with Eu³⁺ for red–green dual marking systems
- Optical probes in coatings and composite materials
- Typical compounds: Terbium acetylacetonate (Tb(acac)₃), Terbium oxide nanoparticles.
Integration into UV-Curable Acrylate Coatings
For next-generation low-silicone, UV-curable acrylates, these rare earth markers are especially attractive:
- They can be incorporated in small amounts without disrupting the curing process.
- Certain organometallic complexes (e.g. β-diketonates) are soluble in acrylates and provide stable luminescence.
- By adjusting the rare earth ion and ligand system, coatings can be tailored for red, orange, or green fluorescence.
Outlook
As industries seek more advanced anti-counterfeiting solutions, sensor platforms, and smart coatings, rare earth fluorescent markers like Eu³⁺, Sm³⁺, and Tb³⁺ will continue to expand in use. At GESmaterials, we are committed to supporting these developments with high-quality rare earth compounds and nanomaterials tailored for research and industrial applications.